这篇文章写于 2019-11-30 可能其中的内容已经发生更改
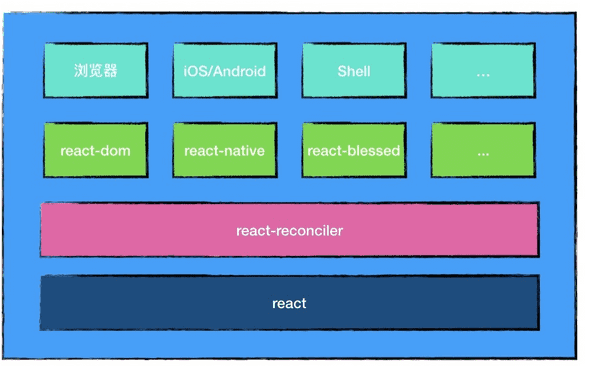
如上图,可以看到 react 实际上分成了几个部分,
-
react
react 本身代码量并相比于整体来说并不算多,他主要的工作就是调用 react-reconciler 的一些接口,定义了一些 Symbol 之类的工作。
-
react-reconciler
那么 react-reconciler 就主要维护 VirtualDOM 树,完成什么时候需要更新,要更新什么之类的操作,你们可能常听到的 Fiber Diff 之类的东西就在这里面。
-
ReactDOM
可以看到这里并排了几个东西 比如 react-dom 对应于浏览器,react-native 对应了移动平台...,其中的 react-dom 就实现了怎样将 react 中的东西渲染到网页上面。
可能上面的东西说起来不怎么具体,那举一些 api 的例子可能能够更清楚的分辨他们
-
主机环境 (dom / native)
- 浏览器
div, span,img...
- Native
View, Text, Image...
-
共用的部分 (reconciler)
- function components
- class components
- props, state
- effects, lifecycles
- key, ref, context
- lazy, error boundaries
- concurrent mode, suspense
其实我们在 npm 安装的时候就只装了 react 和 react-dom,因为 reconciler 是在 react-dom 这个包中有的,但是我们仍然可以单独安装 react-reconciler 来构建我们自己的 render
react-reconciler
react-reconciler 有两种模式
-
mutation mode
view = createView() updateView(view, { color: 'red' })对应到 dom 操作就是
div = document.createElement('div') div.style.color = 'red' -
persistent mode (immutable)
view = createView() view = cloneView(view, { color: 'red' })
现在 ReactNative 正考虑使用后者,据说能提升性能
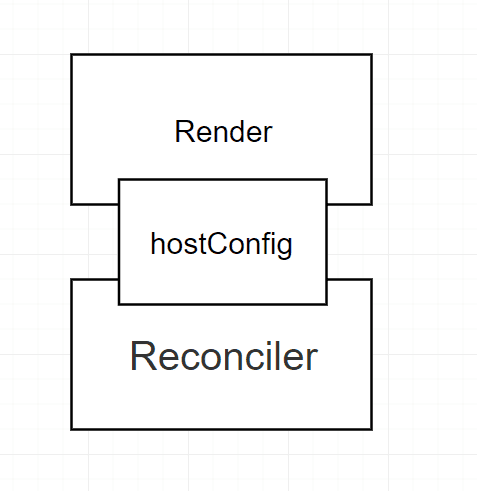
可以看见我们需要定义的就是 hostConfig 部分,我们还是直接开始吧。当一个舒适的 api 仔。
开始
安装 CRA (create react app)
npx create-react-app test-app
cd test-app
npm start安装 react-reconciler
npm i react-reconciler
npm i @types/react-reconciler -D显示元素
src/index.js
import React from 'react';
- import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
+ import ReactDOM from './ReactDOM'
import './index.css';
import App from './App';
import * as serviceWorker from './serviceWorker';
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));src/ReactDOM
import ReactReconciler from 'react-reconciler'
const reconciler = ReactReconciler({
// 定义一些东西怎样与 render 环境进行交互
supportsMutation: true,
/**
* createInstance
* @param type 字符串 eg: img, p, a (这里没有 App 因为 react 已经提前处理了)
* @param props props eg: className, src
* @param rootContainerInstance
* @param hostContext
* @param internalInstanceHandle
* @return {Element}
*/
createInstance (type, props, rootContainerInstance, hostContext, internalInstanceHandle) {
const el = document.createElement(type);
// if (props.className) el.className = props.className
['alt', 'className', 'href', 'rel', 'src', 'target'].forEach(item => {
if (props[item]) el[item] = props[item]
})
return el // 这里 react 并没有规定返回的是什么,也就意味这里可以在这里返回一个你自定的 dom
},
/**
* createTextInstance
* @param text 文字信息,例如下面的 click
* @param rootContainerInstance
* @param hostContext
* @param internalInstanceHandle
* @returns {Text}
*/
createTextInstance (text, rootContainerInstance, hostContext, internalInstanceHandle) {
// <div>click</div>
return document.createTextNode(text)
},
appendChildToContainer (container, child) {
container.appendChild(child)
},
appendChild (parentInstance, child) {
parentInstance.appendChild(child)
},
appendInitialChild (parentInstance, child) {
parentInstance.appendChild(child)
},
prepareUpdate (instance, type, oldProps, newProps, rootContainerInstance, hostContext) {},
commitUpdate (instance, updatePayload, type, oldProps, newProps, internalInstanceHandle) {},
finalizeInitialChildren (parentInstance, type, props, rootContainerInstance, hostContext) {},
getChildHostContext (parentHostContext, type, rootContainerInstance) {},
getPublicInstance (instance) {},
getRootHostContext (rootContainerInstance) {},
prepareForCommit (containerInfo) {},
resetAfterCommit (containerInfo) {},
shouldSetTextContent (type, props) {
return false
},
})
export default {
render (whatToRender, div) {
const container = reconciler.createContainer(div, false, false)
reconciler.updateContainer(whatToRender, container, null, null)
}
}现在就可以看到已经有东西显示在页面上了
事件监听
接下来,我们添加一些事件上去
src/App.js
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import logo from './logo.svg'
import './App.css'
function App () {
+ const [showLogo, setShowLogo] = useState(true)
return (
- <div className="App">
+ <div className="App" onClick={() => setShowLogo(show => !show)}>
<header className="App-header">
- <img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo"/>
+ {showLogo && <img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo"/>}
<p>
Edit <code>src/App.js</code> and save to reload.
</p>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://reactjs.org"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
Learn React
</a>
</header>
</div>
)
}
export default Appsrc/ReactDOM
import ReactReconciler from 'react-reconciler'
const reconciler = ReactReconciler({
// 定义一些东西怎样与 render 环境进行交互
supportsMutation: true,
/**
* createInstance
* @param type 字符串 eg: img, p, a (这里没有 App 因为 react 已经提前处理了)
* @param props props eg: className, src
* @param rootContainerInstance
* @param hostContext
* @param internalInstanceHandle
* @return {Element}
*/
createInstance (type, props, rootContainerInstance, hostContext, internalInstanceHandle) {
const el = document.createElement(type);
['alt', 'className', 'href', 'rel', 'src', 'target'].forEach(item => {
if (props[item]) el[item] = props[item]
})
+ if (props.onClick) el.addEventListener('click', props.onClick)
return el // 这里 react 并没有规定返回的是什么,也就意味这里可以在这里返回一个你自定的 dom
},
/**
* createTextInstance
* @param text 文字信息,例如下面的 click
* @param rootContainerInstance
* @param hostContext
* @param internalInstanceHandle
* @returns {Text}
*/
createTextInstance (text, rootContainerInstance, hostContext, internalInstanceHandle) {
// <div>click</div>
return document.createTextNode(text)
},
appendChildToContainer (container, child) {
container.appendChild(child)
},
appendChild (parentInstance, child) {
parentInstance.appendChild(child)
},
appendInitialChild (parentInstance, child) {
parentInstance.appendChild(child)
},
+ removeChildFromContainer (container, child) {
+ container.removeChild(child)
+ },
+ removeChild (parentInstance, child) {
+ parentInstance.removeChild(child)
+ },
+ insertInContainerBefore (container, child, beforeChild) {
+ container.insertBefore(child, beforeChild)
+ },
+ insertBefore (parentInstance, child, beforeChild) {
+ parentInstance.insertBefore(child, beforeChild)
+ },
prepareUpdate (instance, type, oldProps, newProps, rootContainerInstance, hostContext) {},
commitUpdate (instance, updatePayload, type, oldProps, newProps, internalInstanceHandle) {},
finalizeInitialChildren (parentInstance, type, props, rootContainerInstance, hostContext) {},
getChildHostContext (parentHostContext, type, rootContainerInstance) {},
getPublicInstance (instance) {},
getRootHostContext (rootContainerInstance) {},
prepareForCommit (containerInfo) {},
resetAfterCommit (containerInfo) {},
shouldSetTextContent (type, props) {
return false
},
})
export default {
render (whatToRender, div) {
const container = reconciler.createContainer(div, false, false)
reconciler.updateContainer(whatToRender, container, null, null)
}
}然后我们发现 logo 实现了 toggle 的效果,当然真实情况肯定没有之前我们所写的那么简单,我们最开始学 react 的时候就知道,react 将所有的事件都绑定到顶层的
这里我们可以看到我们并没有写一些与 state 相关的东西,这就说明了 ReactReconciler 帮我们完成了 Diff 之类的东西,这样我们只需指导 react 怎样去处理 dom 就可以了,ReactReconciler 只要是 js runtime 就可以运行,这也提供了 react 能渲染到多个平台上的能力。
更新属性
src/App.js
import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react'
import logo from './logo.svg'
import './App.css'
function App () {
const [showLogo, setShowLogo] = useState(true)
+ const [color, setColor] = useState('red')
+ useEffect(()=>{
+ const colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue']
+ let i = 0
+ let interval = setInterval(()=>{
+ i++
+ setColor(colors[i % 3])
+ }, 1000)
+ return () => clearInterval(interval)
+ })
return (
<div className="App" onClick={() => setShowLogo(show => !show)}>
<header className="App-header">
{showLogo && <img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo"/>}
- <p>
+ <p bgColor={color}>
Edit <code>src/App.js</code> and save to reload.
</p>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://reactjs.org"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
Learn React
</a>
</header>
</div>
)
}
export default Appsrc/ReactDOM
import ReactReconciler from 'react-reconciler'
const reconciler = ReactReconciler({
// 定义一些东西怎样与 render 环境进行交互
supportsMutation: true,
/**
* createInstance
* @param type 字符串 eg: img, p, a (这里没有 App 因为 react 已经提前处理了)
* @param props props eg: className, src
* @param rootContainerInstance
* @param hostContext
* @param internalInstanceHandle
* @return {Element}
*/
createInstance (type, props, rootContainerInstance, hostContext, internalInstanceHandle) {
const el = document.createElement(type);
['alt', 'className', 'href', 'rel', 'src', 'target'].forEach(item => {
if (props[item]) el[item] = props[item]
})
if (props.onClick) el.addEventListener('click', props.onClick)
+ if (props.bgColor) el.style.backgroundColor = props.bgColor
return el // 这里 react 并没有规定返回的是什么,也就意味这里可以在这里返回一个你自定的 dom
},
/**
* createTextInstance
* @param text 文字信息,例如下面的 click
* @param rootContainerInstance
* @param hostContext
* @param internalInstanceHandle
* @returns {Text}
*/
createTextInstance (text, rootContainerInstance, hostContext, internalInstanceHandle) {
// <div>click</div>
return document.createTextNode(text)
},
appendChildToContainer (container, child) {
container.appendChild(child)
},
appendChild (parentInstance, child) {
parentInstance.appendChild(child)
},
appendInitialChild (parentInstance, child) {
parentInstance.appendChild(child)
},
removeChildFromContainer (container, child) {
container.removeChild(child)
},
removeChild (parentInstance, child) {
parentInstance.removeChild(child)
},
insertInContainerBefore (container, child, beforeChild) {
container.insertBefore(child, beforeChild)
},
insertBefore (parentInstance, child, beforeChild) {
parentInstance.insertBefore(child, beforeChild)
},
prepareUpdate (instance, type, oldProps, newProps, rootContainerInstance, hostContext) {
+ let palyload
+ if(oldProps.bgColor !== newProps.bgColor) {
+ palyload = { newBgColor: newProps.bgColor }
+ }
+ return palyload
},
/**
* commitUpdate
* @param instance dom 实例
* @param updatePayload 从 prepareUpdate 返回的
* @param type
* @param oldProps
* @param newProps
* @param internalInstanceHandle
*/
commitUpdate (instance, updatePayload, type, oldProps, newProps, internalInstanceHandle) {
+ if (updatePayload.newBgColor) {
+ instance.style.backgroundColor = updatePayload.newBgColor
+ }
},
finalizeInitialChildren (parentInstance, type, props, rootContainerInstance, hostContext) {},
getChildHostContext (parentHostContext, type, rootContainerInstance) {},
getPublicInstance (instance) {},
getRootHostContext (rootContainerInstance) {},
prepareForCommit (containerInfo) {},
resetAfterCommit (containerInfo) {},
shouldSetTextContent (type, props) {
return false
},
})
export default {
render (whatToRender, div) {
const container = reconciler.createContainer(div, false, false)
reconciler.updateContainer(whatToRender, container, null, null)
}
}这里大概讲一下 hostConfig 定义的东西,也相当于对于前面的一些重新记忆吧,我们先将这些 api 分为以下部分。
| 协调阶段 | 开始提交 | 提交阶段 |
|---|---|---|
| createInstance | prepareCommit | appendChildToContainer |
| createTextInstance | insertBefore | |
| appendInitialChild | insertInContainerBefore | |
| removeChild | ||
| removeChildFromContainer |
import ReactReconciler from 'react-reconciler'
const reconciler = ReactReconciler({
// 定义一些东西怎样与 render 环境进行交互
supportsMutation: true,
/**
* 普通节点实例创建,例如 DOM 的 Element 类型
* @param type 字符串 eg: img, p, a (这里没有 App 因为 react 已经提前处理了)
* @param props props eg: className, src
* @param rootContainerInstance
* @param hostContext
* @param internalInstanceHandle
* @return {Element}
*/
createInstance (type, props, rootContainerInstance, hostContext, internalInstanceHandle) {
const el = document.createElement(type);
['alt', 'className', 'href', 'rel', 'src', 'target'].forEach(item => {
if (props[item]) el[item] = props[item]
})
if (props.onClick) el.addEventListener('click', props.onClick)
if (props.bgColor) el.style.backgroundColor = props.bgColor
return el // 这里 react 并没有规定返回的是什么,也就意味这里可以在这里返回一个你自定的 dom
},
/**
* 文本节点的创建,例如 DOM 的 Text 类型
* @param text 文字信息,例如下面的 click
* @param rootContainerInstance
* @param hostContext
* @param internalInstanceHandle
* @returns {Text}
*/
createTextInstance (text, rootContainerInstance, hostContext, internalInstanceHandle) {
// <div>click</div>
return document.createTextNode(text)
},
// 添加子节点到容器节点(根节点)
// 也就是加载到 document.getElementById('root') 中去
appendChildToContainer (container, child) {
// console.log(container)
container.appendChild(child)
},
// 如果节点在 未挂载 状态下,会调用这个来添加子节点
appendInitialChild (parentInstance, child) {
// console.log(parentInstance)
parentInstance.appendChild(child)
},
// 插入子节点到容器节点(根节点)
insertInContainerBefore (container, child, beforeChild) {
// console.log(container)
container.insertBefore(child, beforeChild)
},
// 插入子节点
insertBefore (parentInstance, child, beforeChild) {
// console.log(parentInstance)
parentInstance.insertBefore(child, beforeChild)
},
// 从容器节点(根节点)中移除子节点
removeChildFromContainer (container, child) {
// console.log(container)
container.removeChild(child)
},
// 删除子节点
removeChild (parentInstance, child) {
// console.log(parentInstance)
parentInstance.removeChild(child)
},
/**
* 准备节点更新. 如果返回空则表示不更新,这时候commitUpdate则不会被调用
* @param instance dom 元素
* @param type div, a
* @param oldProps 以前的 Props
* @param newProps 要更新的 Props
* @param rootContainerInstance
* @param hostContext
* @returns {{newBgColor: *}}
*/
prepareUpdate (instance, type, oldProps, newProps, rootContainerInstance, hostContext) {
let palyload
if(oldProps.bgColor !== newProps.bgColor) {
palyload = { newBgColor: newProps.bgColor }
}
return palyload
},
/**
* commitUpdate
* @param instance dom 实例
* @param updatePayload 从 prepareUpdate 返回的
* @param type div, a ...
* @param oldProps
* @param newProps
* @param internalInstanceHandle
*/
commitUpdate (instance, updatePayload, type, oldProps, newProps, internalInstanceHandle) {
if (updatePayload.newBgColor) {
instance.style.backgroundColor = updatePayload.newBgColor
}
},
finalizeInitialChildren (parentInstance, type, props, rootContainerInstance, hostContext) {},
getChildHostContext (parentHostContext, type, rootContainerInstance) {},
getPublicInstance (instance) {},
getRootHostContext (rootContainerInstance) {},
prepareForCommit (containerInfo) {},
resetAfterCommit (containerInfo) {},
shouldSetTextContent (type, props) {
return false
},
})
export default {
render (whatToRender, div) {
const container = reconciler.createContainer(div, false, false)
reconciler.updateContainer(whatToRender, container, null, null)
}
}然后可以看到这里有很多的 api 都没有用到,实际的 react-dom 肯定特别复杂
然后可能这东西不怎么 practical(实际, 可能不会用上),但是大家应该对 react 有了一点认识了。
Remax
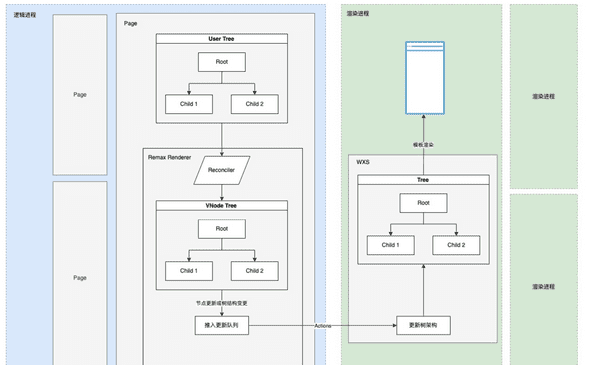
Remax 是蚂蚁金服搞的一个用 react 写小程序的框架,他也是通过编写自己的 react render ,渲染到维护在内存中的一个 vdom,然后再通过 setData 到小程序中的,然后这个项目才刚开始,不像 taro 是一个庞然大物,这里大概说一下他的实现。( taro next 也采用了类似的技术,但 taro 将 dom 的实现抽离,这样就能让 vue 也能用上这种方案)
组成
remax 通过 lerna 进行 monorepo 管理,分为以下部分
remax提供运行时 -- 相当于 react domremax-cli提供构建功能 -- 使用 EJS 生成 小程序的 wxml, wxs...,用 rollup 打包代码
现在主要来讲 Remax
VNode
小程序中我们拿不到 dom,所以就不能像之前那样做 dom 的操作了,然后之前说到了 remax 会在内存中创建一个 vdom,我们先来看看他的 vnode 的代码, 这里只贴了一些主要的代码,并且删除了 TypeScript 的一些东西
...
export default class VNode {
...
// 构造函数
constructor({
id, // 层级 id 会在生成的小程序自定义组件中出现
type, // Text, Image
props,
container, // 上级的容器
}) {
this.id = id;
this.container = container;
this.type = type;
this.props = props;
this.children = [];
}
// 添加节点到父节点中
appendChild(node, immediately) {
node.parent = this;
this.children.push(node);
...
}
// 从父节点中删除节点
removeChild(node, immediately) {
const start = this.children.indexOf(node);
this.children.splice(start, 1);
...
}
...
// **与 dom 不同的 提交更新到 container**
update() {
// root 不会更新,所以肯定有 parent (container)
this.container.requestUpdate(
...
);
}
}可见和 dom 上面能做的操作差不多
HostConfig(react-reconciler)
我们现在有了 vdom,那么我们来看怎么让 react 来操作 vdom,跟我们上面讲的在网页上的 hostConfig 需要定义的东西差不多,下面是 Remax hostConfig 的部分代码
const HostConfig = {
// 创建宿主组件实例
createInstance(type, newProps, container) {
const id = generate();
// 对 props 进行一些处理,如果 newProps 是 function 的话拿到顶部的 context 中进行 callback
const props = processProps(newProps, container, id);
return new VNode({
id,
type,
props,
container,
});
},
// 创建宿主组件文本节点实例
createTextInstance(text: string, container: Container) {
const id = generate();
const node = new VNode({
id,
type: TYPE_TEXT,
props: null,
container,
});
node.text = text;
return node;
},
...
// 添加子节点到容器节点(根节点)
appendChildToContainer(container: any, child: VNode) {
container.appendChild(child);
child.mounted = true;
},
// 删除子节点
removeChild(parent: VNode, child: VNode) {
parent.removeChild(child, false);
},
...
// 提交更新
commitUpdate(node, updatePayload, type, oldProps, newProps) {
node.props = processProps(newProps, node.container, node.id);
node.update();
},
}更新 vdom 到 小程序
remax 在 Container 也就是网页中的 document.getElementById('root')
export default class Container {
...
requestUpdate(
path,
start,
deleteCount,
immediately,
...items: RawNode[]
) {
const update = {
path, // 更新节点的树路径
start, // 更新节点在children中的索引
deleteCount,
items: items.map(normalizeRawNode), // 主要对 props 进行一些操作, 比如 className => class
};
if (immediately) { // 马上执行更新
this.updateQueue.push(update);
this.applyUpdate();
} else { // 进入队列中
if (this.updateQueue.length === 0) {
// 这里为什么是0, 因为 Promise 执行肯定在我们看到的代码之后,不为 0 的话 上一次的更新还未执行完
// 比如一次更新(之前的东西已经执行完了) 那么队列的长度就为 0
// 然后就进入这个 if 分支
// 放入 promise
// 然后执行其他代码
// 执行完其他代码
// 执行 () => this.applyUpdate()
Promise.resolve().then(() => this.applyUpdate()); // 放到 Promise 中
}
this.updateQueue.push(update);
}
}
applyUpdate() {
...
const action = { // 发送给小程序的对象
type: 'splice',
payload: this.updateQueue.map(update => ({
path: stringPath(update.path),
start: update.start,
deleteCount: update.deleteCount,
item: update.items[0],
})),
id: generateActionId(),
};
// this.context 就是小程序实例
this.context.setData({ action: tree }); // setData 到小程序中
this.updateQueue = [];
}
...
}小程序渲染
我们已经把数据给到了小程序,那么小程序这里是怎样渲染成真正的元素。
我们都知道小程序是以页面为基本单位,我们先来看 pages 是怎么样的
这里使用了 ejs 大家大概看看
<wxs src="<%= jsHelper %>" module="helper" />
<import src="<%= baseTemplate %>"/>
<template is="REMAX_TPL" data="{{tree: helper.reduce(action)}}" />生成之后是这个样子
<wxs src="../../helper.wxs" module="helper" />
<import src="../../base.wxml"/>
<template is="REMAX_TPL" data="{{tree: helper.reduce(action)}}" />wxs 可能大家之前之前不知道,wxs(qs, sjs) 是运行在小程序的渲染线程的被阉割的 js runtime 具体可以看 uni-app 写的文章 ,能减少通时的消耗的消耗,所以把小程序这边的 vdom 放在这里面
helper.wxs
var tree = {
root: {
children: [],
},
};
...
function reduce(action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'splice':
for (var i = 0; i < action.payload.length; i += 1) {
var value = get(tree, action.payload[i].path); // 通过 path 拿到对应的 vnode
if (action.payload[i].item) { // 进行一些处理
value.splice(
action.payload[i].start,
action.payload[i].deleteCount,
action.payload[i].item
);
} else {
value.splice(action.payload[i].start, action.payload[i].deleteCount);
}
set(tree, action.payload[i].path, value); // 将生成的进行替换
}
return tree; // 返回回去
default:
return tree;
}
}
...
module.exports = {
reduce: reduce,
};base.wxml
定义了一些 image,text 等组件
<template name="REMAX_TPL"> // 每个 page 的顶部模板
<block wx:for="{{tree.root.children}}" wx:key="{{id}}">
<template is="REMAX_TPL_1_CONTAINER" data="{{i: item}}" />
</block>
</template>
...
// image 的模板,并且是 page 最顶部的那个,因为微信小程序不能递归的调用,所以只能每层的template都不一样
<template name="REMAX_TPL_1_image">
<image>
<block wx:for="{{i.children}}" wx:key="{{id}}">
<template is="REMAX_TPL_2_CONTAINER" data="{{i: item}}" />
</block>
</image>
</template>
...
<template name="REMAX_TPL_2_image">
<image >
<block wx:for="{{i.children}}" wx:key="{{id}}">
<template is="REMAX_TPL_3_CONTAINER" data="{{i: item}}" />
</block>
</image>
</template>
...
...
...
...
// 所以一个页面只能套 20 层,不是就没 template 了
<template name="REMAX_TPL_20_image">
<image >
<block wx:for="{{i.children}}" wx:key="{{id}}">
<template is="REMAX_TPL_21_CONTAINER" data="{{i: item}}" />
</block>
</image>
</template>但是这有一些缺点,可能会影响性能,但是其实性能在出现之前都不是问题。
-
一是因为 Remax 相较于浏览器多了两个或者三个 vdom
- react 维护的 vdom
- remax 在逻辑进程维护的 vdom
- remax 在 wxs 中的 vdom
- (可能有) 小程序自己的 vdom
但是好处是我们在 setData 是经过 diff 的最小的数据量,而我们使用了 setData 也就意味者想用 react 来管理动画是不可能的了,但是目前没有办法改善,因为 wxs 定义的模块只能在 wxml 中用,也就是 remax 不能直接访问 wxs 的函数,即 逻辑进程维护的 vdom 必须存在然后通过 setData 传递。
- 二是微信小程序限制,不能模板不能递归,只能套 20 层